Prominent superficial temporal artery and transient ischaemea
Published: 05/01/2012
Authors: Cook CM
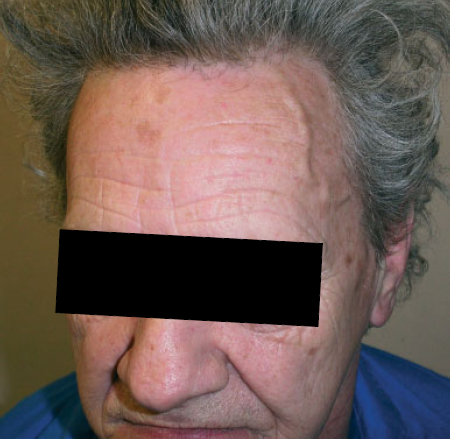
A 63-year-old man presented with transient dysarthria and blurred vision. Clinical examination was unremarkable apart from a prominent superficial temporal artery on the left side of the scalp. A carotid duplex scan revealed a normal common and external carotid on the left, but the internal carotid was occluded from its origin. On the right side the common carotid artery was also occluded. Right-sided cerebral perfusion was thus dependant on the left external carotid artery via retrograde flow through the superficial temporal system to the carotid bulb, before diverting into the right internal carotid artery – manifest simply as a prominent left superficial temporal artery.

