Snapshot quiz 16/3
Published: 03/18/2016
Authors: Grifson JJ, Anand L and Kannan DG
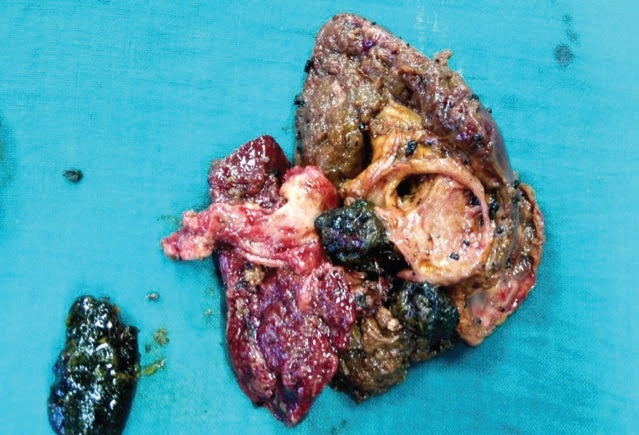
The specimen shows the resected left liver lobe from a patient with hepatolithiasis and lobar atrophy. Intrahepatic stones (hepatolithiasis) are concretions in the bile ducts proximal to the confluence. Stones may form primarily or can result secondary to choledochal cyst or anastomotic stricture. These stonesmay be asymptomatic or can present with recurrent cholangitis or obstructive jaundice, secondary cirrhosis or cholangiocarcinoma. Asymptomatic patients are usually observed. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic stone removal is possible in patients who are symptomatic. Resection is indicated in a symptomatic patient, when there is atrophy of a lobe or a segment, or suspicion of cholangiocarcinoma.

