Snapshot quiz 17/4
Published: 04/06/2017
Authors: Chia C and Ho T
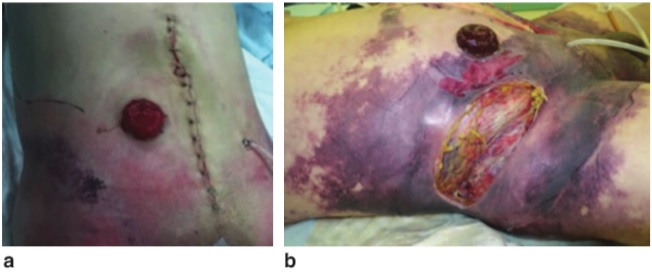
The diagnosis is necrotizing fasciitis. The patient underwent emergency laparotomy to exclude an anastomotic leak. Dishwasher fluid was seen on incising the abdominal wall and aggressive surgical debridement was performed. Blood and tissue culture subsequently isolated Escherichia coli. Twelve hours after surgery, the skin lesions were extensive with progression of gangrene (b). Despite repeat surgical debridement, he subsequently died from septic shock. Necrotizing fasciitis is a fulminant infection that can occur early after surgery. E. coli is a rare monomicrobial causative agent. Mortality remains high despite aggressive surgical debridement.

